Novel Water-Tight Beaver Dam Analogs (WTBDA) to Restore Eroded Seasonal Creeks in Drain Tile Zones, to Permanent Beaver Wetlands.
A Review of Two Novel Water-Tight Beaver Dam Analogs (WTBDA) to Restore Eroded Seasonal Creeks in Drain Tile Zones, to Permanent Beaver Wetlands.
Author
Christian Sorflaten, Beaver Wetland Professional, Bachelor in Science
6/15/2022
Abstract
Introduction
Hypothesis
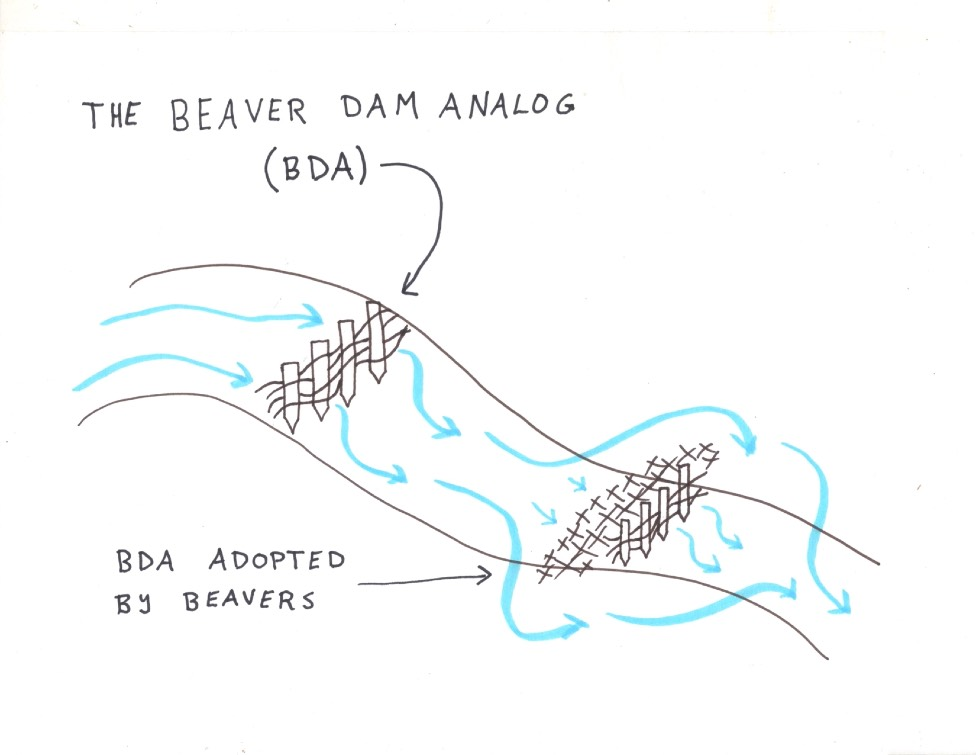
Figure 1. Traditional Beaver Dam Analog (BDA)
Scientific Method - Log Spillway Design
- Identify a natural log bridge across the creek or precision-drop a tree. Pin with stakes and mimic nearby flood tolerant natural structures.
- Drive vertical posts into the creek bed, supported by the natural log spillway bridge. Scrap ash logs milled to 3”x3” and up to 9’ long were utilized. Ends were cut to point and driven in with a Titan gas powered post pounder
- Invasive honeysuckle and overgrowth were cleared for wetland sun. Dormant native wetland species were observed and expected to return.
- Weave branches into BDA - beaver dam analog.
- Use 4wd dump truck to deposit water tight clay plug.
- Dump gravel and rocks on top of and around clay plug to prevent erosion of clay. Fill in the area between clay plug and BDA.
- Plant scrub willow and native wetland seeds into dam and bank for habitat and future beaver food.
- Willow stakes 2’-8’ long were used. Thicker, longer and straighter posts are ideal. Ends sharpened. Scrub willow is a beaver’s favorite food and gets about 15’ tall. Species vary and include red, white, black and coyote willow in the west.
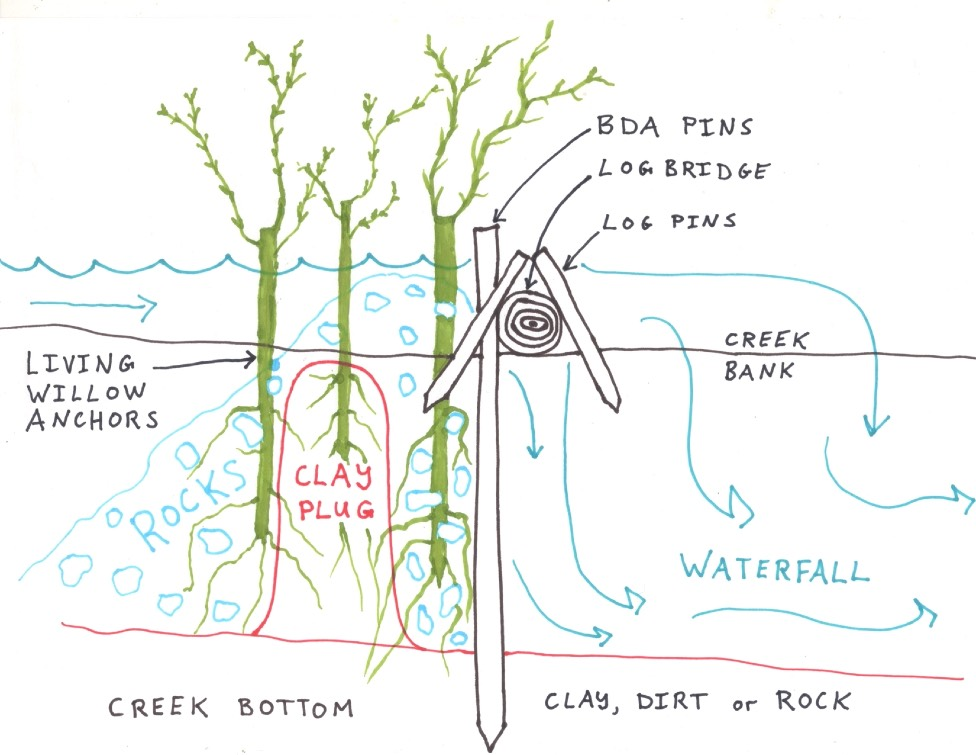
Figure 2: Water Tight Beaver Dam Analog (Log Spillway WTBDA)
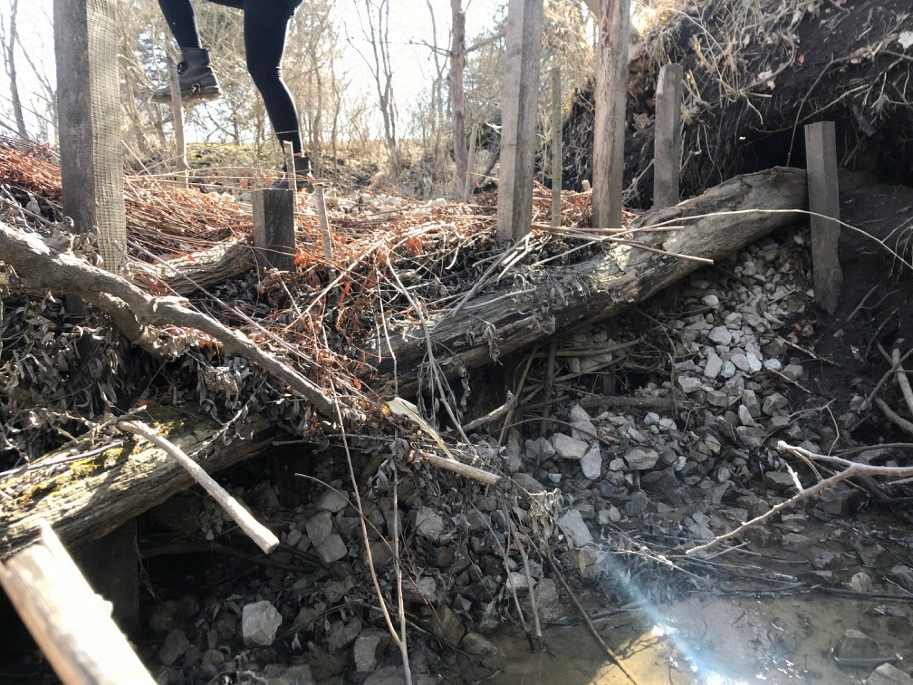
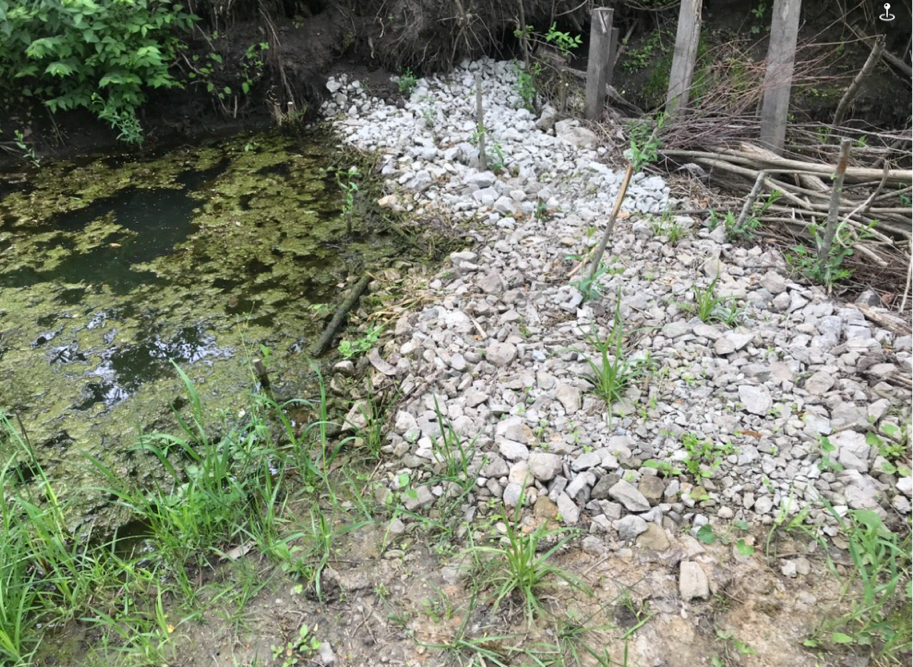


Figure 3: WTBDA After 1 Year.
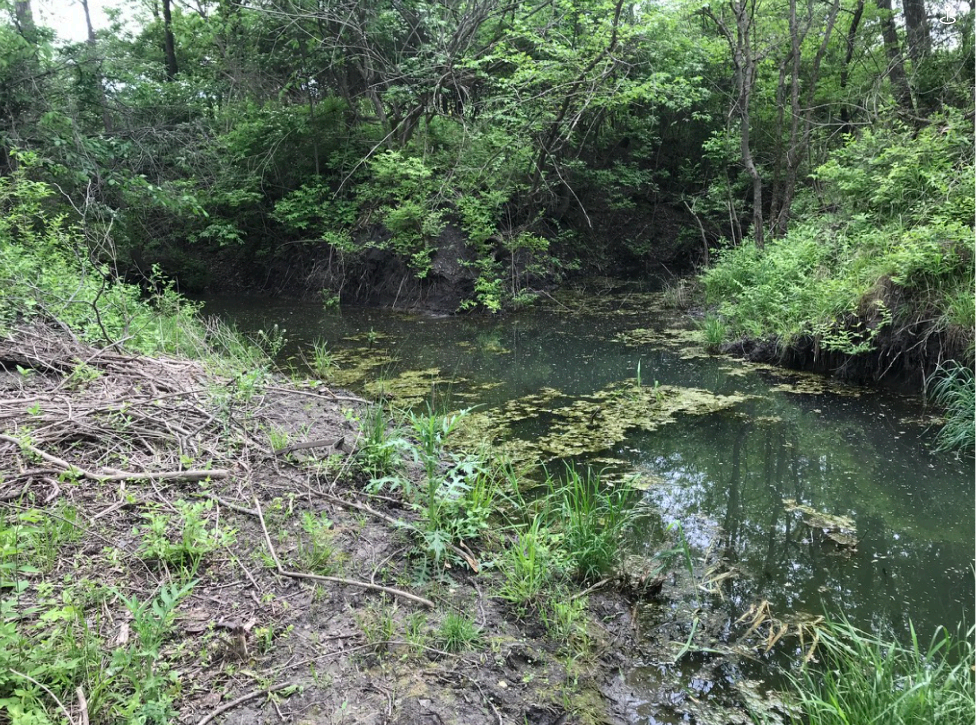

Figure 4: WTBDA Upstream View
- Identify a spot with easy access for dump truck and potential for successive pools.
- Dump 3 loads of clay at 1.5 tons per load to achieve desired water depth.
- Tamp and pack clay between each load.
- Dump and spread rocks, 1 load 3” gravel, 1 load 1” gravel.
- Add native wetland grass seed.
- Use mini sledge to drive in willow stakes in 1/sf grid.
- Use grafting wax or non-toxic glue to seal open wounds on willow.
- Build a “safety dam” downstream of berm to create a scour pool during high flow.
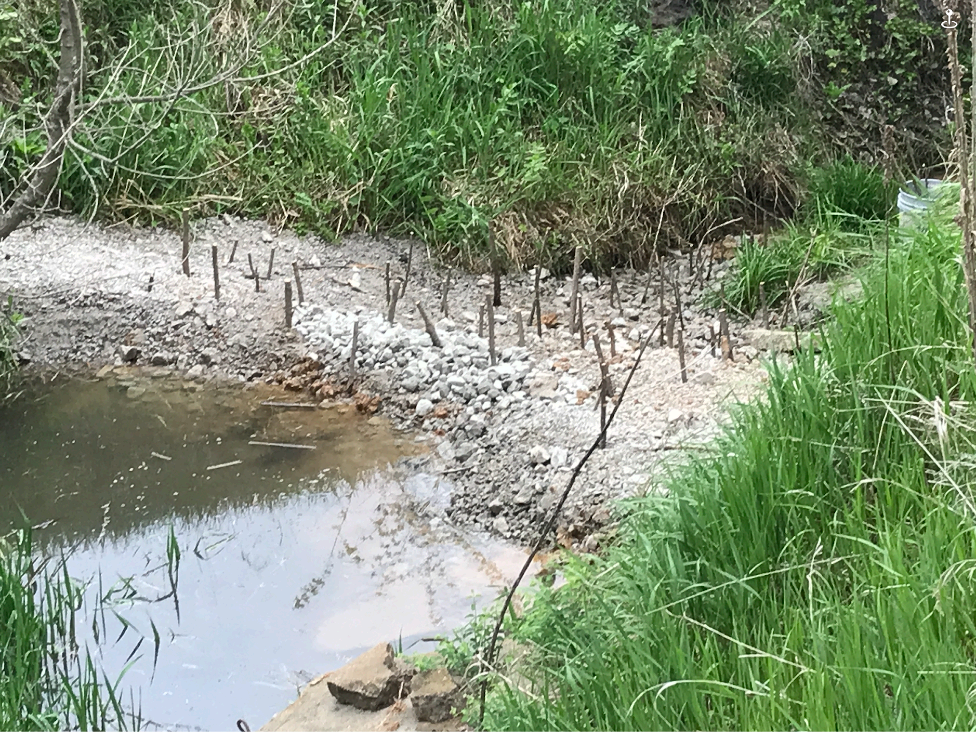

Figure 5: Berm Style WTBDA Upstream Side

Figure 6: Berm Style, Downstream Side with Safety Dam
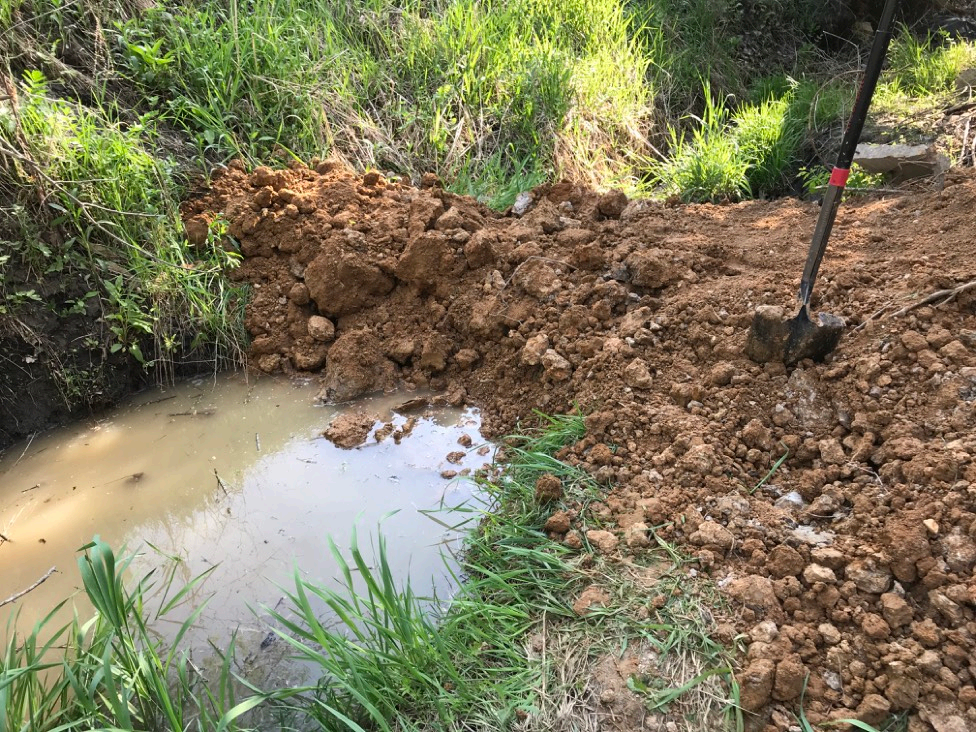

Figure 7: Clay Berm Under Construction
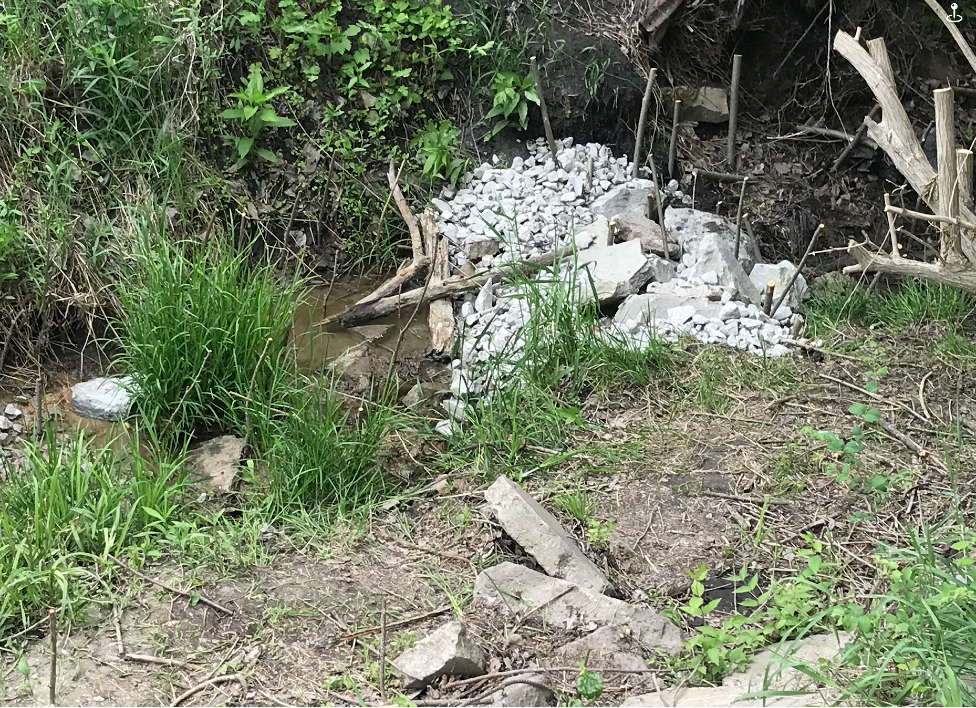

Figure 8: Safety Dam Closeup
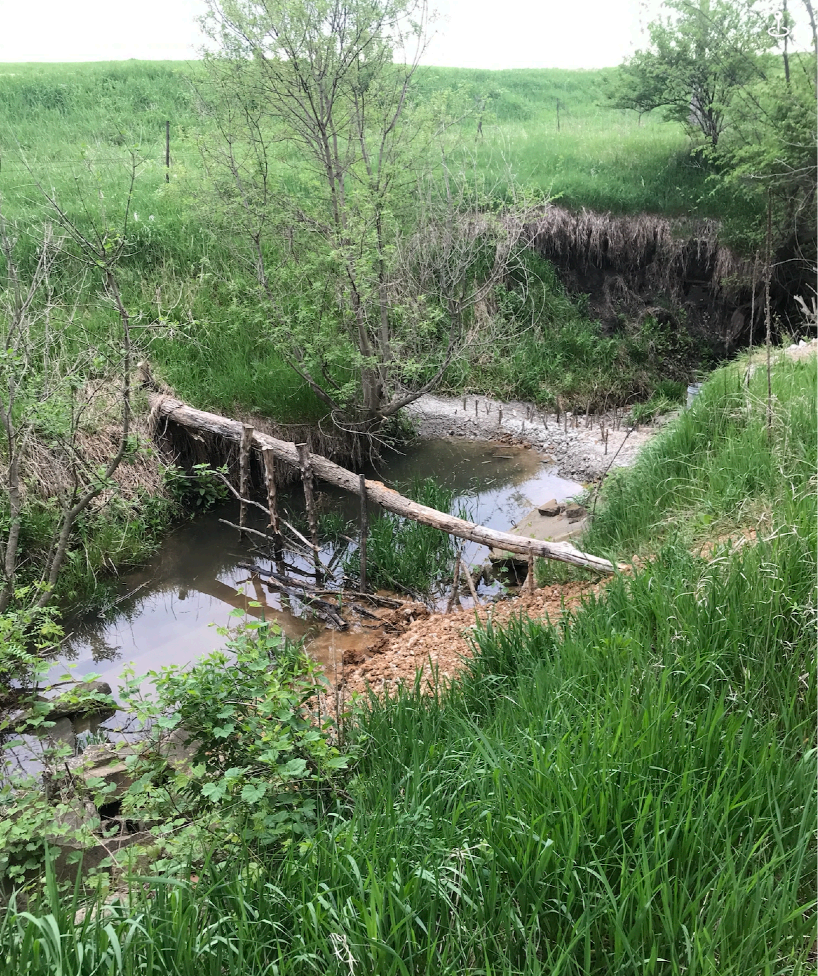

Figure 9: Upstream View with Abandoned Standards BDA
Results
- Water increased from 1 inch to 2-3 feet deep.
- Observed fish, tadpoles and frogs grow to normal size in the first week.
- Observed dragonflies in 2nd week.
- Greater varieties of butterflies and moths.
- In about 3 years, beavers are expected to arrive and maintain dams.
- Tree protection and water leveling devices can be used if needed.
- Mosquitoes are expected to reduce due to increased predators.
- Native fish can migrate up the dam during high flow.
- Crayfish burrowed around the clay plug, through the topsoil and leaked water downstream. This appeared to not disturb the WTBDA structure.
- Touch up rocks and heavier rocks may be placed around edges after heavy rainfall as needed. Piles of extra rocks are recommended.
- Creek widening into braided channels was observed, as well as saturation of lower bank soil. Existing grasses and mosses prevented erosion during high flow.
- Little to no erosion was observed and sediment appeared.
- Pools formed for about 100’ in both upstream forks and reached the road culvert.
- 1.5 tons was comfortably loaded into 3/4 ton Chevy diesel 4WD. Mudding tires are used to reduce soil compaction and ruts. Care was taken to not bottom out and only cosmetic scratches were observed to the truck.
- Erosion and dam failure appeared to start at the downstream end. Therefore the “safety-dam” was developed and tested to disburse kinetic energy of bottom ends of successive BDAs.
Notes
- Invasive carp theoretically cannot go up the natural dam, thereby encouraging emergent vegetation.
- Beaver colonies can occupy dam complexes for over 30 years and then repopulate years later after tree food has grown back.
- Beavers mate for life and offspring will look to populate upstream and downstream areas first.
- They are non-violent and build scented mounds to mark their territory.
- High beaver concentration areas like the midwest can expect nuisance beavers to comb the entire area every 2-3 years, seeking out potential habitat that is rare to find. Currently, man-made ponds are usually the best option.
- Clay and rocks are piled up higher along edges in a H formation such that if failure occurs, it will not cause bank erosion.
Cost Analysis
Conclusion
The WTBDA was developed over 4 years of research and development in
Iowa. Previously, BDAs washed away, beavers ate willow BDAs, undesired
creek widening and everything imaginable. It took about 2-3 man hours to
shovel a load out of the truck, therefore a Pierce-Arrow hydraulic dump kit
was installed. A good investment for contractors, due to rust-proofing and
easy underbody pressure washing. As with standard beaver dams,
WTBDAs work better in succession. With downstream pools touching
upstream dams. In conclusion, these WTBDA designs are suitable for any
type of grant for restoration and water quality including Gulf of Mexico
dead zone projects. Also, the berm style is recommended for most
applications due to less tools required and simpler construction. Berm
style is recommended for first time builders and also the standard BDA
with log bridge for bigger watersheds in drain tile zones.
https://lowtechpbr.restoration.usu.edu



